24
Dimensionality Reduction
Singular Value Decomposition
Theory
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) is a fundamental matrix factorization technique that decomposes any matrix into three component matrices. It's used for dimensionality reduction, data compression, noise reduction, and latent semantic analysis.
Visualization
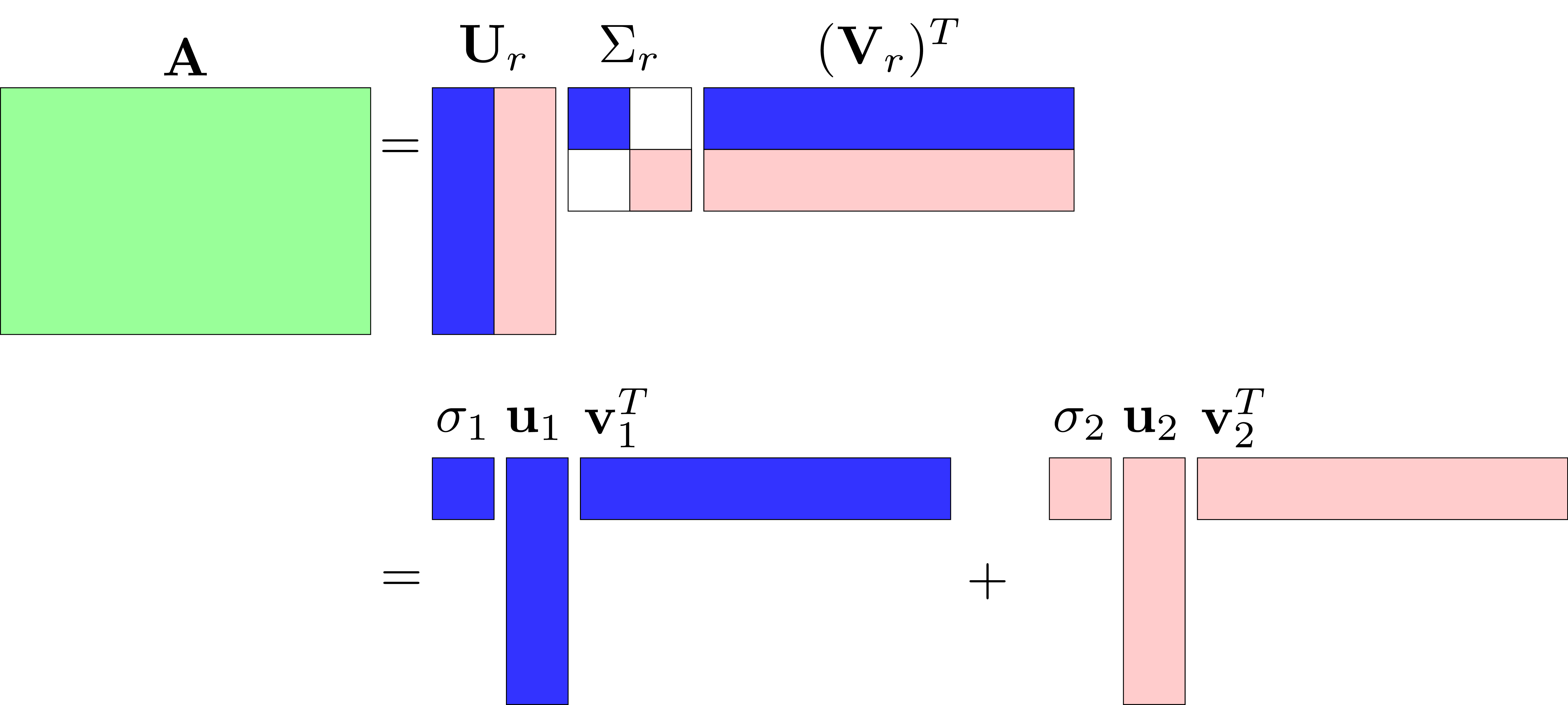
Mathematical Formulation
Decomposition: A = UΣVᵀ • U: m×m orthogonal (left singular vectors) • Σ: m×n diagonal (singular values, descending) • V: n×n orthogonal (right singular vectors) Low-Rank Approximation: A ≈ UₖΣₖVₖᵀ (keep top k singular values)
Code Example
import numpy as np
from scipy.linalg import svd
# Create sample matrix
np.random.seed(42)
A = np.random.randn(5, 4)
print("Original Matrix A:")
print(A.round(2))
print(f"Shape: {A.shape}")
# Perform SVD
U, s, Vt = svd(A, full_matrices=True)
print(f"\nU shape: {U.shape}")
print(f"s shape: {s.shape}")
print(f"Vt shape: {Vt.shape}")
# Verify reconstruction
Sigma = np.zeros((A.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
Sigma[:len(s), :len(s)] = np.diag(s)
A_reconstructed = U @ Sigma @ Vt
reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(A - A_reconstructed)
print(f"\nReconstruction error: {reconstruction_error:.10f}")
# Truncated SVD (dimensionality reduction)
k = 2 # Keep top 2 components
U_k = U[:, :k]
s_k = s[:k]
Vt_k = Vt[:k, :]
A_k = U_k @ np.diag(s_k) @ Vt_k
print(f"\nLow-rank approximation (k={k}):")
print(A_k.round(2))
# Compression ratio
original_size = A.size
compressed_size = k * (A.shape[0] + A.shape[1] + 1)
ratio = original_size / compressed_size
print(f"\nCompression ratio: {ratio:.2f}x")