7
Neural Networks
Perceptron Learning Algorithm
Theory
The Perceptron is one of the simplest types of artificial neural networks, designed for binary classification. It's a linear classifier that learns a decision boundary to separate two classes. The perceptron only converges for linearly separable data.
Visualization
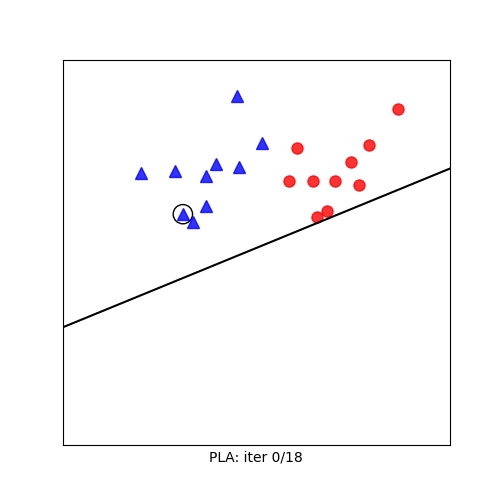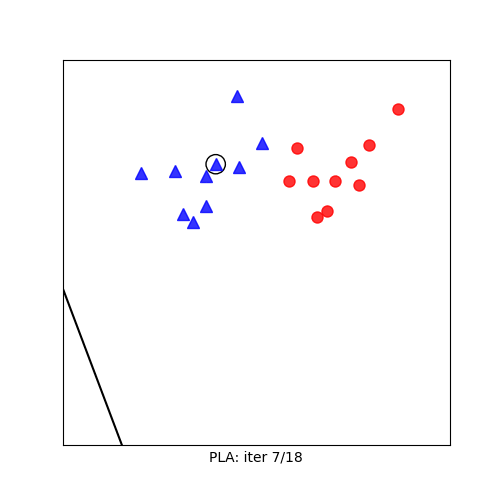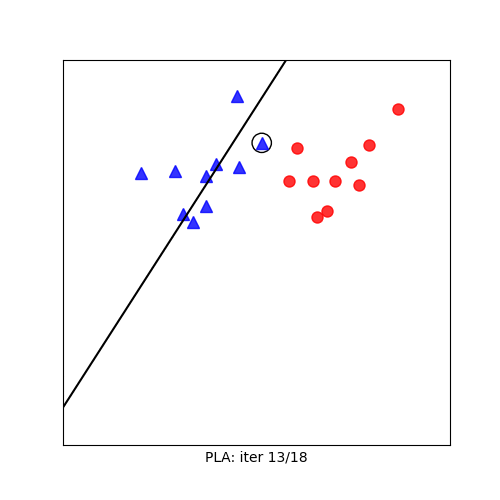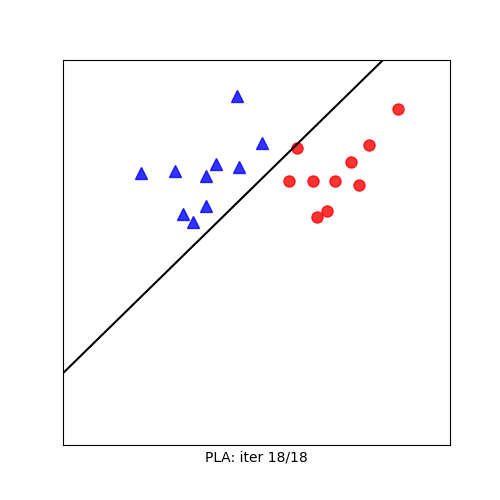
Mathematical Formulation
Decision Function:
ŷ = sign(w·x + b)
Update Rule (if misclassified):
w = w + y·x
b = b + y
Where y ∈ {-1, +1}Code Example
import numpy as np
class Perceptron:
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, n_iterations=1000):
self.lr = learning_rate
self.n_iter = n_iterations
self.weights = None
self.bias = None
def fit(self, X, y):
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
# Initialize weights
self.weights = np.zeros(n_features)
self.bias = 0
# Convert labels to {-1, 1}
y_ = np.where(y <= 0, -1, 1)
# Training
for _ in range(self.n_iter):
for idx, x_i in enumerate(X):
# Calculate prediction
linear_output = np.dot(x_i, self.weights) + self.bias
y_pred = np.sign(linear_output)
# Update rule
if y_[idx] * y_pred <= 0:
self.weights += self.lr * y_[idx] * x_i
self.bias += self.lr * y_[idx]
def predict(self, X):
linear_output = np.dot(X, self.weights) + self.bias
return np.sign(linear_output)
# Example
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=100, n_features=2,
centers=2, random_state=42)
y = np.where(y == 0, -1, 1)
perceptron = Perceptron()
perceptron.fit(X, y)
predictions = perceptron.predict(X)
accuracy = np.mean(predictions == y)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.3f}")