23
Recommender Systems
Matrix Factorization Collaborative Filtering
Theory
Matrix Factorization decomposes the user-item rating matrix into lower-dimensional latent factor matrices, capturing hidden patterns in preferences. It handles sparse data well and scales to large datasets.
Visualization
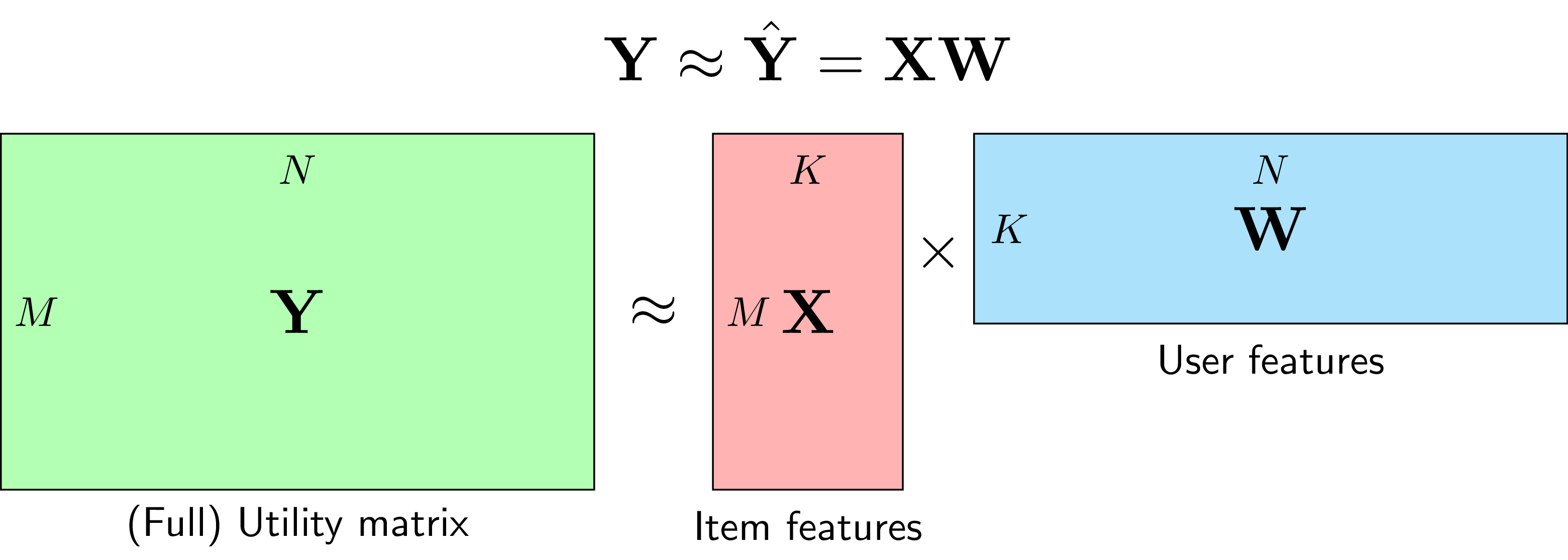
Mathematical Formulation
Formulation: R ≈ P × Qᵀ R: m×n rating matrix P: m×k user factors Q: n×k item factors Optimization (SGD): minimize Σ(rᵤᵢ - pᵤ·qᵢ)² + λ(||pᵤ||² + ||qᵢ||²)
Code Example
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse.linalg import svds
# Sample ratings
R = np.array([
[5, 4, 0, 0, 3],
[4, 0, 0, 5, 4],
[0, 5, 4, 0, 5],
[3, 0, 5, 4, 0]
])
print("Original Rating Matrix:")
print(R)
# Matrix Factorization using SVD
n_factors = 2
# Center ratings
R_mean = R[R > 0].mean()
R_centered = R.copy()
R_centered[R > 0] -= R_mean
# SVD
U, sigma, Vt = svds(R_centered, k=n_factors)
# Reconstruct
R_pred = U @ np.diag(sigma) @ Vt + R_mean
R_pred = np.clip(R_pred, 1, 5)
print("\nPredicted Ratings:")
print(R_pred.round(2))
# Alternative: Gradient Descent
def matrix_factorization_gd(R, k=2, steps=5000,
alpha=0.002, beta=0.02):
"""Train with gradient descent"""
m, n = R.shape
P = np.random.rand(m, k)
Q = np.random.rand(n, k)
for step in range(steps):
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if R[i, j] > 0:
eij = R[i, j] - np.dot(P[i], Q[j])
P[i] += alpha * (2 * eij * Q[j] - beta * P[i])
Q[j] += alpha * (2 * eij * P[i] - beta * Q[j])
return P, Q.T
P, Qt = matrix_factorization_gd(R)
R_pred_gd = P @ Qt
print("\nGradient Descent Predictions:")
print(R_pred_gd.round(2))