1
Basics
Linear Regression
Theory
Linear regression is one of the most fundamental algorithms in machine learning. It models the relationship between a dependent variable y and one or more independent variables X by fitting a linear equation to observed data. The goal is to find the optimal weights that minimize the prediction error, typically measured using Mean Squared Error (MSE).
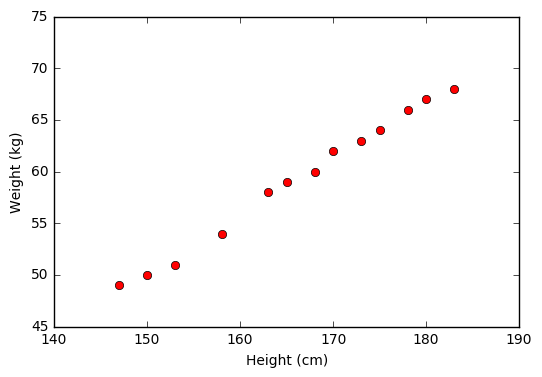
Visualization
Mathematical Formulation
ŷ = w₀ + w₁x₁ + w₂x₂ + ... + wₙxₙ MSE = (1/n) Σ(yᵢ - ŷᵢ)²
Code Example
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generate sample data
X = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]])
y = np.array([2, 4, 5, 4, 5])
# Create and train the model
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
# Make predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X)
# Visualize
plt.scatter(X, y, color='blue', label='Data')
plt.plot(X, y_pred, color='red', label='Fit')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
print(f"Coefficient: {model.coef_[0]:.2f}")
print(f"Intercept: {model.intercept_:.2f}")