15
Optimization
Convex Optimization Problems
Theory
A convex optimization problem has a convex objective function and convex constraints. These problems can be solved efficiently with guaranteed global optimality. Many ML algorithms are formulated as convex optimization problems.
Visualization
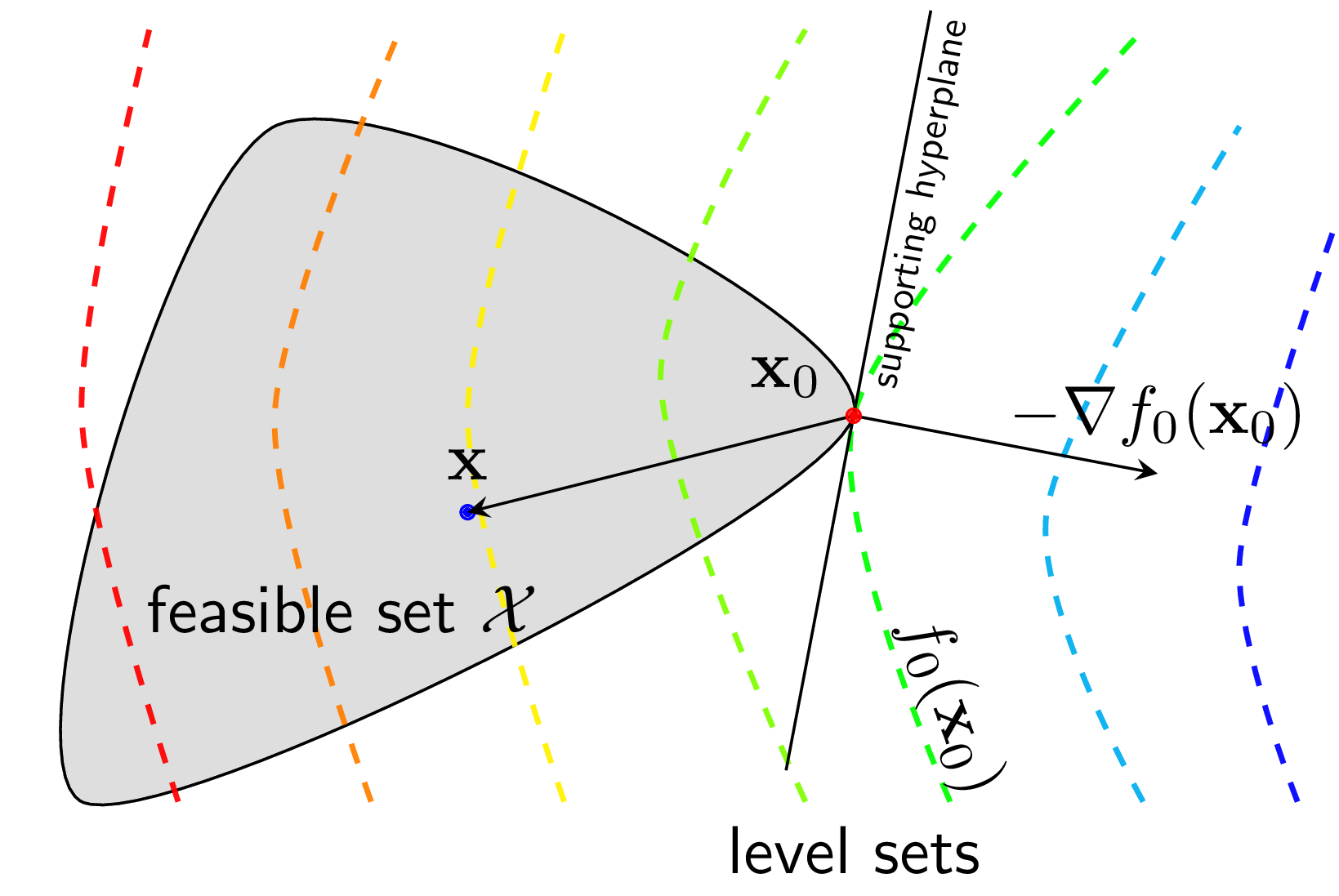
Mathematical Formulation
Standard Form:
minimize f(x)
subject to gᵢ(x) ≤ 0, i = 1,...,m
hⱼ(x) = 0, j = 1,...,p
where f and gᵢ are convex, hⱼ are affine
Key Properties:
• Local minimum = Global minimum
• Efficient algorithms (polynomial time)
• Gradient descent convergesCode Example
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import numpy as np
# Example: Least Squares (convex)
# minimize ||Ax - b||²
# Generate problem data
np.random.seed(42)
A = np.random.randn(20, 10)
b = np.random.randn(20)
# Define objective and gradient
def objective(x):
residual = A @ x - b
return 0.5 * np.sum(residual**2)
def gradient(x):
return A.T @ (A @ x - b)
# Solve
result = minimize(objective, x0=np.zeros(10),
jac=gradient, method='BFGS')
print(f"Optimal value: {result.fun:.4f}")
print(f"Solution norm: {np.linalg.norm(result.x):.4f}")
# Compare with closed-form solution
x_optimal = np.linalg.lstsq(A, b, rcond=None)[0]
print(f"Closed-form solution norm: {np.linalg.norm(x_optimal):.4f}")